一: ansible 的概述
1. ansible简介
Ansible是一款为类Unix系统开发的自由开源的配置和自动化工具。
它用Python写成,类似于saltstack和Puppet,但是有一个不同和优点是我们不需要在节点中安装任何客户端。
它使用SSH来和节点进行通信。Ansible基于 Python paramiko 开发,分布式,无需客户端,轻量级,配置语法使用 YMAL 及 Jinja2模板语言,更强的远程命令执行操作。
2. 官方网站
我们可以看到上面的红帽标志,红帽公司于2015年10月收购了ansible,而ansible成立于2013年。
3. ansible 的特点
1、部署简单,没有客户端,只需在主控端部署Ansible环境,被控端无需做任何操作;
2. 模块化:调用特定的模块,完成特定任务
3. 默认使用SSH协议对设备进行管理;
4. 主从集中化管理;
5、配置简单、功能强大、扩展性强;
6、支持API及自定义模块,可通过Python轻松扩展;
7、通过Playbooks来定制强大的配置、状态管理
8. 对云计算平台、大数据都有很好的支持;
9. 具有幂等性:一个操作在一个主机上执行一遍和执行N遍的结果是一样的
ansible是基于模块工作的,本身没有批量部署的能力。真正具有批量部署的是ansible所运行的模块,ansible只是提供一种框架。主要包括:
(1)、连接插件connection plugins:负责和被监控端实现通信;
(2)、host inventory:指定操作的主机,是一个配置文件里面定义监控的主机;
(3)、各种模块核心模块、command模块、自定义模块;
(4)、借助于插件完成记录日志邮件等功能;
(5)、playbook:剧本执行多个任务时,非必需可以让节点一次性运行多个任务
4. ansible的工作机制
Ansible 在管理节点将 Ansible 模块通过 SSH 协议推送到被管理端执行,执行完之后自动删除,可以使用 SVN 等来管理自定义模块及编排
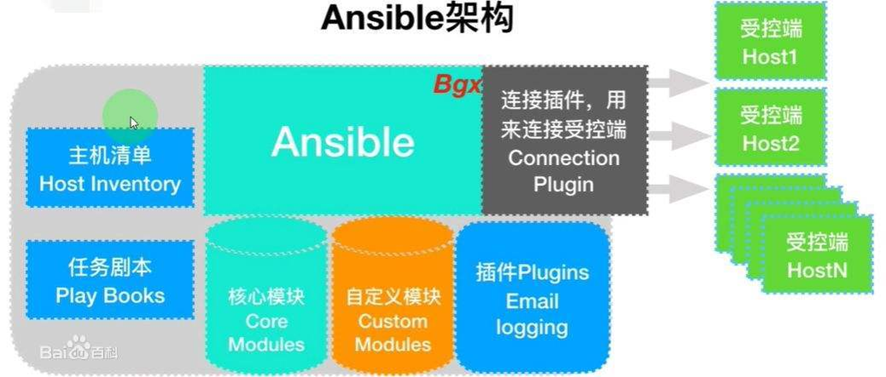
由图可以看出Ansible的组成由一下模块组成:
| Ansible: ansible的核心模块 Host Inventory:主机清单,也就是被管理的主机列表 Playbooks:ansible的剧本,可想象为将多个任务放置在一起,一块执行 Core Modules:ansible的核心模块 Custom Modules:自定义模块 Connection Plugins:连接插件,用于与被管控主机之间基于SSH建立连接关系 Plugins:其他插件,包括记录日志等 |
二. Asible的安装
1. 设置EPEL仓库
Ansible仓库默认不在yum仓库中,因此我们需要使用下面的命令启用epel仓库
| [root@localhost ~]# yum install epel-release -y |
2. 使用yum安装Ansible
| [root@localhost ~]# yum install ansible -y |
3. 查看ansible的版本
| [root@localhost ~]# ansible –version ansible 2.9.27 config file = /etc/ansible/ansible.cfg configured module search path = [u’/root/.ansible/plugins/modules’, u’/usr/share/ansible/plugins/modules’] ansible python module location = /usr/lib/python2.7/site-packages/ansible executable location = /usr/bin/ansible python version = 2.7.5 (default, Nov 16 2020, 22:23:17) [GCC 4.8.5 20150623 (Red Hat 4.8.5-44)] |
ansible的命令参数
anisble命令语法: ansible [-i 主机文件] [-f 批次] [组名] [-m 模块名称] [-a 模块参数]
| 参数 功能 -v 详细模式,如果执行成功,输出详细结果 -i 指定host文件路径,默认在/etc/ansible/hosts -f,-forks=NUM NUM默认是整数5,指定fork开启同步进程的个数 -m 指定使用的module名称,默认command模块 -a 指定模块的参数 -k 提示输入SSH密码,而不是使用基于ssh密钥认证 -sudo 指定使用sudo获取root权限 -K 提示输入sudo密码 -u 指定移动端的执行用户 -C 测试命令执行会改变什么内容,不会真正的去执行 |
ansible-doc 详细参数
[root@localhost ~]# ansible-doc -l
列出所有模块列表
| fortios_router_community_list Configure community lists in Fortinet’s FortiOS and FortiGate azure_rm_devtestlab_info Get Azure DevTest Lab facts ecs_taskdefinition register a task definition in ecs avi_alertscriptconfig Module for setup of AlertScriptConfig Avi RESTful Object tower_receive Receive assets from Ansible Tower netapp_e_iscsi_target NetApp E-Series manage iSCSI target configuration azure_rm_acs Manage an Azure Container Service(ACS) instance fortios_log_syslogd2_filter Filters for remote system server in Fortinet’s FortiOS and FortiGate junos_rpc Runs an arbitrary RPC over NetConf on an Juniper JUNOS device na_elementsw_vlan NetApp Element Software Manage VLAN pn_ospf CLI command to add/remove ospf protocol to a vRouter pn_snmp_vacm CLI command to create/modify/delete snmp-vacm cp_mgmt_service_sctp Manages service-sctp objects on Check Point over Web Services API onyx_ospf Manage OSPF protocol on Mellanox ONY netwodevices : |
| 指定查看某个模块的参数 ansible-doc -s 模块名字 [root@localhost ~]# ansible-doc -s onyx_ospf – name: Manage OSPF protocol on Mellanox ONYX network devices onyx_ospf: interfaces: # List of interfaces and areas. Required if `state=present’. ospf: # (required) OSPF instance number 1-65535 router_id: # OSPF router ID. Required if `state=present’. state: # OSPF state. |
三. ansible的使用
1. 基于端口,用户,密码定义主机清单
格式:
ansible基于ssh连接-i (inventory)参数后指定的远程主机时,也可以写端口,用户,密码。
如:
ansible_ssh_port: 指定ssh端口 ansible_ssh_user:指定 ssh 用户 ansible_ssh_pass: 指定 ssh 用户登录是认证密码(明文密码不安全) ansible_sudo_pass: 指明 sudo 时候的密码
添加的内容如下:
[root@localhost ~]# vim /etc/ansible/hosts
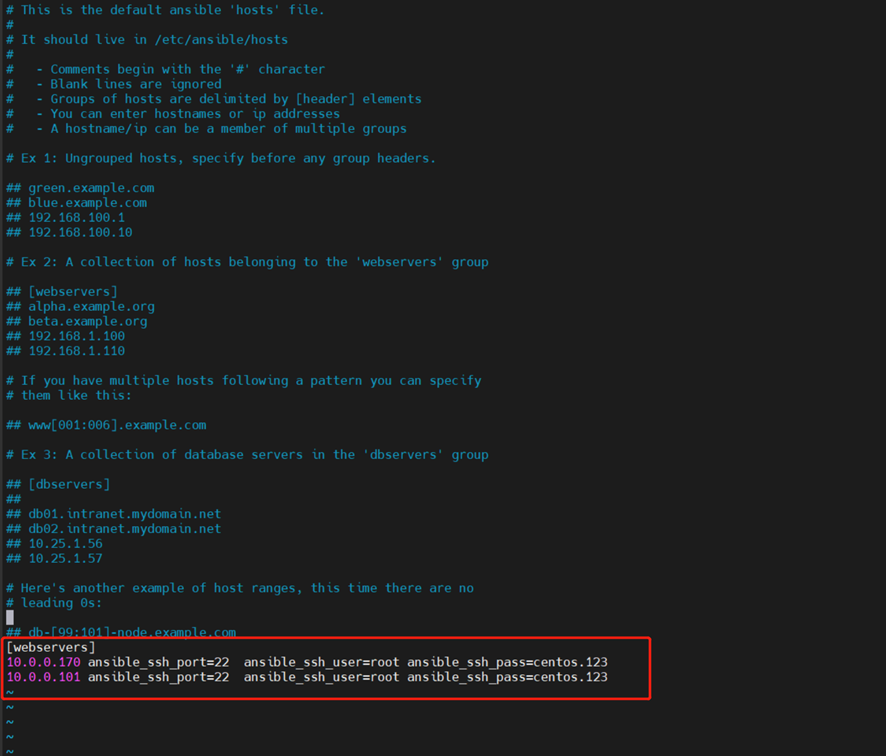
查看添加的主机:
| [root@localhost ~]# grep -v ^# /etc/ansible/hosts |grep -v ^$ [webservers] 10.0.0.170 ansible_ssh_port=22 ansible_ssh_user=root ansible_ssh_pass=centos.123 10.0.0.101 ansible_ssh_port=22 ansible_ssh_user=root ansible_ssh_pass=centos.123 |
直接添加到文件文末就可以;
测试主机的连通性(如果现实连接失败可以先用ssh连接一次)
| [root@localhost ~]# ansible -i /etc/ansible/hosts webservers -m ping 10.0.0.170 | SUCCESS => { “ansible_facts”: { “discovered_interpreter_python”: “/usr/bin/python” }, “changed”: false, “ping”: “pong” } 10.0.0.101 | SUCCESS => { “ansible_facts”: { “discovered_interpreter_python”: “/usr/bin/python” }, “changed”: false, “ping”: “pong” } |
查看组下所有的IP:
| [root@localhost ~]# ansible all –list hosts (2): 10.0.0.170 10.0.0.101 |
2. 基于ssh密钥来访问定义主机清单
设置密钥
| [root@localhost ~]# ssh-keygen Generating public/private rsa key pair. 生成公共/私有rsa密钥对 Enter file in which to save the key (/root/.ssh/id_rsa): 输入保存密钥的文件 Enter passphrase (empty for no passphrase): 输入密码短语(无密码短语为空) Enter same passphrase again: 再次输入相同的密码短语 Your identification has been saved in /root/.ssh/id_rsa. 您的身份已保存在/root/.ssh/id_rsa中。 Your public key has been saved in /root/.ssh/id_rsa.pub. 你的公钥已保存在/root/.ssh/id_rsa.pub中 The key fingerprint is: 关键加密信息是: SHA256:Y3hgjgCBDKFh48+yoT58opV+BV8v9ErrEx7lB1u/rns root@localhost.localdomain The key’s randomart image is: 密钥的随机图像是 +—[RSA 2048]—-+ |X= | |=+. | |… o | | o..+ oo o . | | o o.oooS= + . | |. +. oo=.= . . | |o.o . o * . . | |.* .. = E | |o.=. … o=. | +—-[SHA256]—–+ |
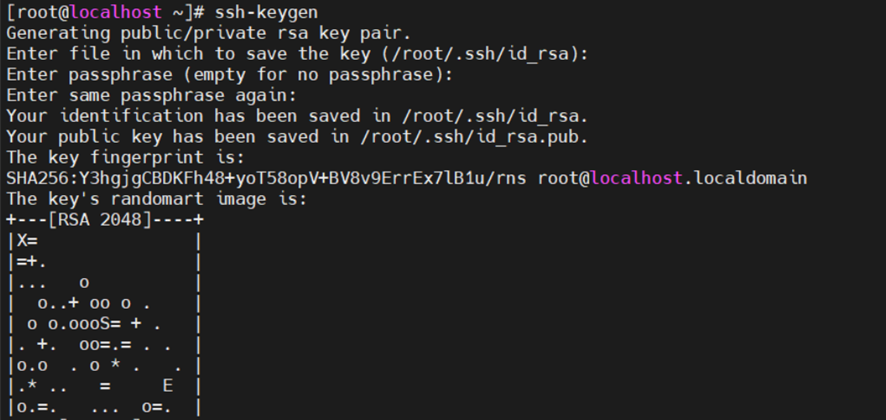
拷贝密钥并测试
| [root@localhost ~]# ssh-copy-id root@10.0.0.170 /usr/bin/ssh-copy-id: INFO: Source of key(s) to be installed: “/root/.ssh/id_rsa.pub” /usr/bin/ssh-copy-id: INFO: attempting to log in with the new key(s), to filter out any that are already installed /usr/bin/ssh-copy-id: INFO: 1 key(s) remain to be installed — if you are prompted now it is to install the new keys root@10.0.0.170’s password: “输入登录密码” Number of key(s) added: 1 Now try logging into the machine, with: “ssh ‘root@10.0.0.170′” and check to make sure that only the key(s) you wanted were added. **登陆测试:** [root@localhost ~]# ssh 10.0.0.170 Last login: Tue Oct 11 11:54:49 2022 from 10.0.0.252 |
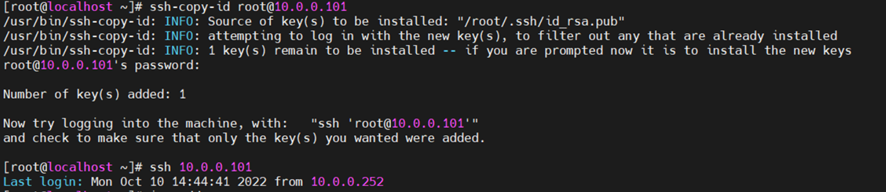
10.0.0.101服务器也发送密钥
[root@localhost ~]# ssh-copy-id root@10.0.0.101
修改hosts
[root@localhost ~]# vim /etc/ansible/hosts
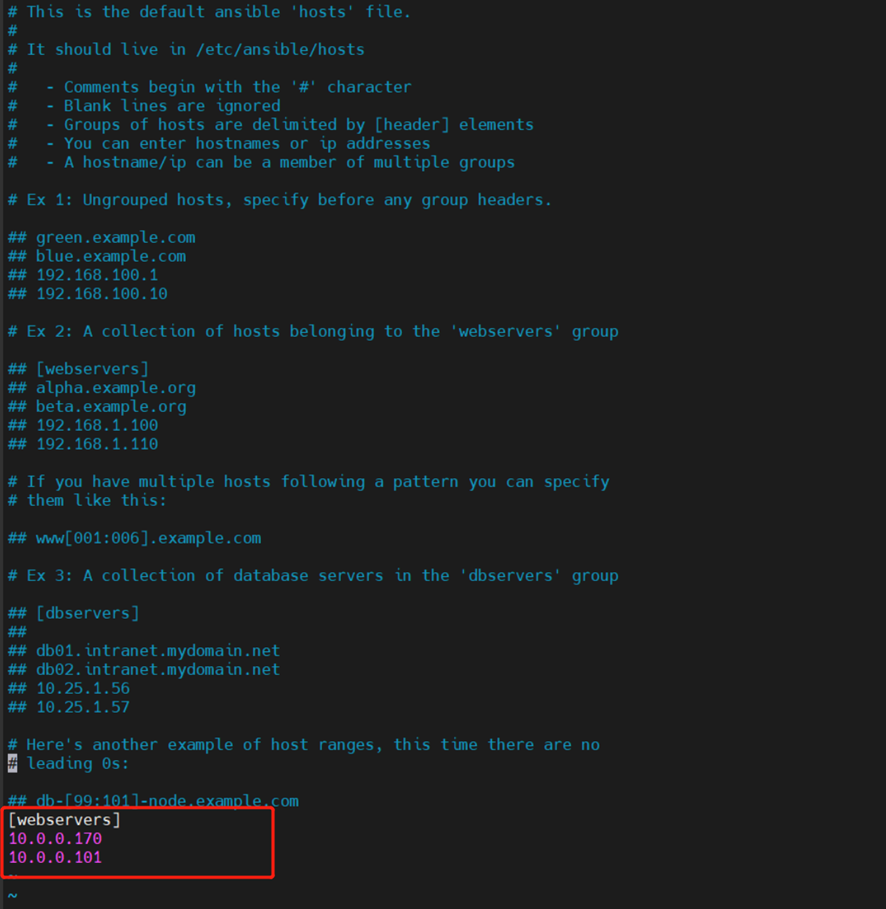
查看配置文件中刚刚修改的内容
| [root@localhost ~]# grep -v “^#” /etc/ansible/hosts |grep -v “^$” [webservers] 10.0.0.170 10.0.0.101 |
ansible远程执行命令测试
ping模块 主要用来检测网络的连通性 command模块,执行shell命令
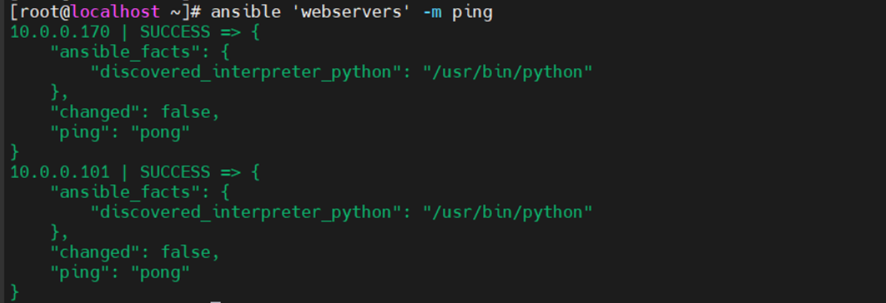
使用ping检查‘webservers’或者ansible节点的连通性。
| [root@localhost ~]# ansible -i /etc/ansible/hosts ‘webservers’ -m ping 10.0.0.170 | SUCCESS => { “ansible_facts”: { “discovered_interpreter_python”: “/usr/bin/python” }, “changed”: false, “ping”: “pong” } 10.0.0.101 | SUCCESS => { “ansible_facts”: { “discovered_interpreter_python”: “/usr/bin/python” }, “changed”: false, “ping”: “pong” } |
这条命令我们也可以不指定hosts,效果是一样的,我们只要指定组即可
| [root@localhost ~]# ansible ‘webservers’ -m ping 10.0.0.170 | SUCCESS => { “ansible_facts”: { “discovered_interpreter_python”: “/usr/bin/python” }, “changed”: false, “ping”: “pong” } 10.0.0.101 | SUCCESS => { “ansible_facts”: { “discovered_interpreter_python”: “/usr/bin/python” }, “changed”: false, “ping”: “pong” } |
有时候我们为了方便阅读也把主机组名写在最后面
webservers 这个组名,放在最后面
| [root@localhost ~]# ansible -m command -a “uptime” ‘webservers’ 10.0.0.170 | CHANGED | rc=0 >> 14:17:49 up 41 days, 30 min, 3 users, load average: 0.00, 0.01, 0.05 10.0.0.101 | CHANGED | rc=0 >> 17:07:41 up 41 days, 19:07, 3 users, load average: 0.00, 0.01, 0.05 |
案例1: 检查节点的内存情况
| [root@localhost ~]# ansible -m command -a “free -m ” ‘webservers’ 10.0.0.170 | CHANGED | rc=0 >> total used free shared buff/cache available Mem: 1838 269 97 16 1470 1409 Swap: 1 0 1 10.0.0.101 | CHANGED | rc=0 >> total used free shared buff/cache available Mem: 1838 194 404 16 1238 1455 Swap: 2047 0 2047 |
案例2:给节点增加用户
| [root@localhost ~]# ansible -m command -a “useradd jchj” ‘webservers’ 10.0.0.170 | CHANGED | rc=0 >> 10.0.0.101 | CHANGED | rc=0 >> |
查看是否创建用户成功
| [root@localhost ~]# ansible -m command -a “id jchj” ‘webservers’ 10.0.0.170 | CHANGED | rc=0 >> uid=1000(jchj) gid=1000(jchj) groups=1000(jchj) 10.0.0.101 | CHANGED | rc=0 >> uid=1000(jchj) gid=1000(jchj) groups=1000(jchj) |
四. ansible的高级用法
1. ansible的常用模块
1) ansible的3个远程模块的区别
command : ansible的默认模块,不指定-m参数的时候,使用的就是command模块; 常见的命令都可以使用,但命令的执行不是通过shell来执行的,所以< > | and & z这些操作都不可以,不支持管道,没法批量执行命令
shell模块:
使用shell模块的时候默认是通过/bin/sh来执行的,所以在终端输入的各种命令都可以使用
scripts模块:
使用scripts模块可以在本地写一个脚本,在远程服务器上执行
案例1:使用shell模块的案例
| [root@localhost ~]# ansible -i /etc/ansible/hosts webservers -m shell -a “source ~/.bash_profile && df -h|head -n 1” 10.0.0.170 | CHANGED | rc=0 >> Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on 文件系统 容量 已用 可用 已用% 挂载点 10.0.0.101 | CHANGED | rc=0 >> Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on 文件系统 容量 已用 可用 已用% 挂载点 |
注意: shell也可以把一个脚本copy到远程端然后再执行,但这样的话就需要调用两次ansible,所以script的出现就解决了这个问题;
案例2:使用script 模块
先写一个脚本:
[root@localhost ~]# vim ceshi.sh
| #!/bin/bash date hostname echo “江城决的小站脚本测试” |
[root@localhost ~]# chmod +x ceshi.sh 给予执行权限
[root@localhost ~]# cp ceshi.sh /etc/ansible/ 把脚本拷贝至ansible目录下不然有可能会因为权限问题执行失败.
执行查看结果:
| [root@localhost ~]# ansible -i /etc/ansible/hosts webservers -m script -a “/etc/ansible/ceshi.sh” 10.0.0.170 | CHANGED => { “changed”: true, “rc”: 0, “stderr”: “Shared connection to 10.0.0.170 closed.\r\n”, “stderr_lines”: [ “Shared connection to 10.0.0.170 closed.” ], “stdout”: “Tue Oct 11 14:40:04 CST 2022\r\nlocalhost.localdomain\r\n江城决的小站脚本测试\r\n”, “stdout_lines”: [ “Tue Oct 11 14:40:04 CST 2022”, “localhost.localdomain”, “江城决的小站脚本测试” ] } 10.0.0.101 | CHANGED => { “changed”: true, “rc”: 0, “stderr”: “Shared connection to 10.0.0.101 closed.\r\n”, “stderr_lines”: [ “Shared connection to 10.0.0.101 closed.” ], “stdout”: “Mon Oct 10 17:29:56 CST 2022\r\nlocalhost.localdomain\r\n江城决的小站脚本测试\r\n”, “stdout_lines”: [ “Mon Oct 10 17:29:56 CST 2022”, “localhost.localdomain”, “江城决的小站脚本测试” ] } |
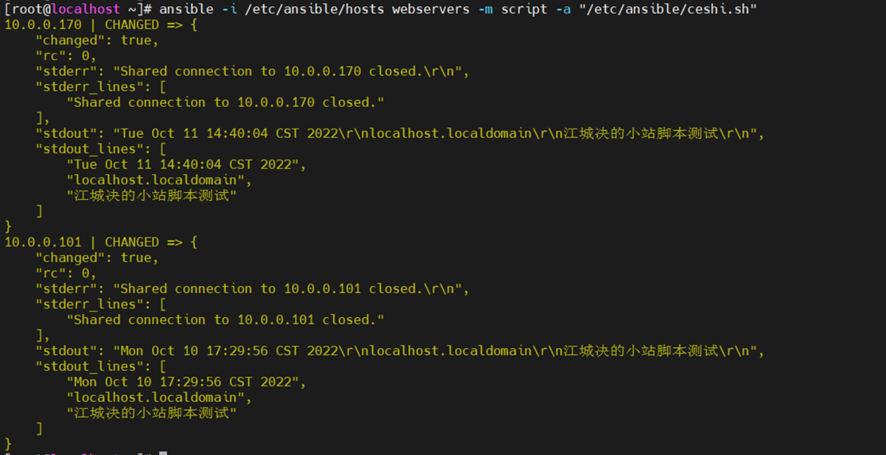
可以看到已经执行成功
2) copy模块的使用
copy模块:实现主控端向目标主机拷贝文件,类似scp功能
案例1: 把ansible主机的/etc/hosts 拷贝到主机组机器中的/root/下
| [root@localhost ~]# ansible -i /etc/ansible/hosts webservers -m copy -a “src=/etc/hosts dest=/root owner=root group=root mode=0777” 10.0.0.170 | CHANGED => { “ansible_facts”: { “discovered_interpreter_python”: “/usr/bin/python” }, “changed”: true, “checksum”: “7335999eb54c15c67566186bdfc46f64e0d5a1aa”, “dest”: “/root/hosts”, “gid”: 0, “group”: “root”, “md5sum”: “54fb6627dbaa37721048e4549db3224d”, “mode”: “0777”, “owner”: “root”, “size”: 158, “src”: “/root/.ansible/tmp/ansible-tmp-1665470828.03-4933-181533222504853/source”, “state”: “file”, “uid”: 0 } 10.0.0.101 | CHANGED => { “ansible_facts”: { “discovered_interpreter_python”: “/usr/bin/python” }, “changed”: true, “checksum”: “7335999eb54c15c67566186bdfc46f64e0d5a1aa”, “dest”: “/root/hosts”, “gid”: 0, “group”: “root”, “md5sum”: “54fb6627dbaa37721048e4549db3224d”, “mode”: “0777”, “owner”: “root”, “secontext”: “system_u:object_r:admin_home_t:s0”, “size”: 158, “src”: “/root/.ansible/tmp/ansible-tmp-1665470828.19-4935-83457666727272/source”, “state”: “file”, “uid”: 0 } |
查看是否执行成功:
| [root@localhost ~]# ansible -m command -a “ls /root/hosts” ‘webservers’ 10.0.0.170 | CHANGED | rc=0 >> /root/hosts 10.0.0.101 | CHANGED | rc=0 >> /root/hosts |
注意: command 不能使用ll命令,但可以使用ls -l的命令
| [root@localhost ~]# ansible -m command -a “ls -l /root/hosts” ‘webservers’ 10.0.0.170 | CHANGED | rc=0 >> -rwxrwxrwx 1 root root 158 Oct 11 14:43 /root/hosts 10.0.0.101 | CHANGED | rc=0 >> -rwxrwxrwx. 1 root root 158 Oct 10 17:33 /root/hosts |
3. file模块
案例5 给文件设置权限
| [root@localhost ~]# ansible -i /etc/ansible/hosts webservers -m file -a “ path=/root/hosts mode=0755″ 10.0.0.170 | CHANGED => { “ansible_facts”: { “discovered_interpreter_python”: “/usr/bin/python” }, “changed”: true, “gid”: 0, “group”: “root”, “mode”: “0755”, “owner”: “root”, “path”: “/root/hosts”, “size”: 158, “state”: “file”, “uid”: 0 } 10.0.0.101 | CHANGED => { “ansible_facts”: { “discovered_interpreter_python”: “/usr/bin/python” }, “changed”: true, “gid”: 0, “group”: “root”, “mode”: “0755”, “owner”: “root”, “path”: “/root/hosts”, “secontext”: “system_u:object_r:admin_home_t:s0”, “size”: 158, “state”: “file”, “uid”: 0 } |
查看权限:
| [root@localhost ~]# ansible -m command -a “ls -l /root/hosts” ‘webservers’ 10.0.0.170 | CHANGED | rc=0 >> -rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 158 Oct 11 14:43 /root/hosts 10.0.0.101 | CHANGED | rc=0 >> -rwxr-xr-x. 1 root root 158 Oct 10 17:33 /root/hosts |
4. stat模块获取远程文件信息
案例6 获取文件信息
| [root@localhost ~]# ansible -i /etc/ansible/hosts webservers -m stat -a “path=/root/hosts” 10.0.0.170 | SUCCESS => { “ansible_facts”: { “discovered_interpreter_python”: “/usr/bin/python” }, “changed”: false, “stat”: { “atime”: 1665470634.914, “attr_flags”: “”, “attributes”: [], “block_size”: 4096, “blocks”: 8, “charset”: “us-ascii”, “checksum”: “7335999eb54c15c67566186bdfc46f64e0d5a1aa”, “ctime”: 1665470761.759, “dev”: 37, “device_type”: 0, “executable”: true, “exists”: true, “gid”: 0, “gr_name”: “root”, “inode”: 86048, “isblk”: false, “ischr”: false, “isdir”: false, “isfifo”: false, “isgid”: false, “islnk”: false, “isreg”: true, “issock”: false, “isuid”: false, “mimetype”: “text/plain”, “mode”: “0755”, “mtime”: 1665470634.638, “nlink”: 1, “path”: “/root/hosts”, “pw_name”: “root”, “readable”: true, “rgrp”: true, “roth”: true, “rusr”: true, “size”: 158, “uid”: 0, “version”: “2993”, “wgrp”: false, “woth”: false, “writeable”: true, “wusr”: true, “xgrp”: true, “xoth”: true, “xusr”: true } } 10.0.0.101 | SUCCESS => { “ansible_facts”: { “discovered_interpreter_python”: “/usr/bin/python” }, “changed”: false, “stat”: { “atime”: 1665394426.785, “attr_flags”: “”, “attributes”: [], “block_size”: 4096, “blocks”: 8, “charset”: “us-ascii”, “checksum”: “7335999eb54c15c67566186bdfc46f64e0d5a1aa”, “ctime”: 1665394553.585, “dev”: 64768, “device_type”: 0, “executable”: true, “exists”: true, “gid”: 0, “gr_name”: “root”, “inode”: 8606222, “isblk”: false, “ischr”: false, “isdir”: false, “isfifo”: false, “isgid”: false, “islnk”: false, “isreg”: true, “issock”: false, “isuid”: false, “mimetype”: “text/plain”, “mode”: “0755”, “mtime”: 1665394426.622, “nlink”: 1, “path”: “/root/hosts”, “pw_name”: “root”, “readable”: true, “rgrp”: true, “roth”: true, “rusr”: true, “size”: 158, “uid”: 0, “version”: “18446744072842500691”, “wgrp”: false, “woth”: false, “writeable”: true, “wusr”: true, “xgrp”: true, “xoth”: true, “xusr”: true } } |
5. get_url 模块
实现远程主机下载指定的url地址,支持sha256sum文件校验
案例7
| ansible -i /etc/ansible/hosts webservers -m get_url -a “url=https://dl.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/epel-release-latest-7.noarch.rpm dest=/tmp/ mode=0440 force=yes” |
注:url=https://xxx 的等号=前后不能有空格
扩展:查看force=yes的作用
6. yum模块
yum模块linux平台软件包管理。
yum模块可以提供的status状态: latest ,present,installed #这三个代表安装;removed, absent #这两个是卸载
案例8 使用yum模块安装httpd
ansible -i /etc/ansible/hosts webservers -m yum -a “name=httpd state=latest”
7. cron模块远程管理主机crontab配置
案例9: 增加每30分钟执行 echo”江城决的小站脚本测试”
ansible -i /etc/ansible/hosts webservers -m cron -a “name=‘list dir’ minute=’*/30’ job=‘echo 江城决的小站脚本测试”’”
8. service 远程管理主机系统服务模块
service模块常用参数:
(1)、name参数:此参数用于指定需要操作的服务名称,比如 nginx,httpd。
(2)、state参数:此参数用于指定服务的状态
比如,我们想要启动远程主机中的httpd,则可以将 state 的值设置为 started;
如果想要停止远程主机中的服务,则可以将 state 的值设置为 stopped。
此参数的可用值有 started、stopped、restarted(重启)、reloaded。
enabled参数:此参数用于指定是否将服务设置为开机 启动项,设置为 yes 表示将对应服务设置为开机启动,设置为 no 表示不会开机启动。
注:想使用service模块启动服务,被启动的服务,必须可以使用service 命令启动或关闭
案例10 使用service模块重启httpd
| [root@localhost ~]# ansible -i /etc/ansible/hosts webservers -m service -a “name=httpd state=restarted” |
9. user模块 管理远程主机的用户
案例11: 使用user模块创建一个用户jchj
| [root@localhost ~]# ansible -i /etc/ansible/hosts webservers -m user -a “name=jchj state=present” 10.0.0.101 | SUCCESS => { “ansible_facts”: { “discovered_interpreter_python”: “/usr/bin/python” }, “append”: false, “changed”: false, “comment”: “”, “group”: 1000, “home”: “/home/jchj”, “move_home”: false, “name”: “jchj”, “shell”: “/bin/bash”, “state”: “present”, “uid”: 1000 } 10.0.0.170 | SUCCESS => { “ansible_facts”: { “discovered_interpreter_python”: “/usr/bin/python” }, “append”: false, “changed”: false, “comment”: “”, “group”: 1000, “home”: “/home/jchj”, “move_home”: false, “name”: “jchj”, “shell”: “/bin/bash”, “state”: “present”, “uid”: 1000 } |
五. playbooks的介绍
1) 在playbooks 中定义任务:
– name: task description #任务描述信息
module_name: module_args #需要使用的模块名字: 模块参数
2) ansible-playbook 执行 命令:
ansible-playbook site.yml
playbook是由一个或多个”play”组成的列表。play的主要功能在于将事先归为一组的主机装扮成事先通过ansible中的task定义好的角色。
github上提供了大量的实例供大家参考: https://github.com/ansible/ansible-examples
使用playbook 批量部署多台LAMP环境
Playbook常用文件夹作用介绍:
files:存放需要同步到异地服务器的源码文件及配置文件;
handlers:当服务的配置文件发生变化时需要进行的操作,比如:重启服务,重新加载配置文件,handlers [‘hændləz] 处理程序
meta:角色定义,可留空;
tasks:需要进行的执行的任务;
templates:用于执行程序安装的模板文件,一般为脚本;
vars:本次安装定义的变量
我们还可以使用playbook创建一个LAMP构建的任务或是部署k8s及集群。
后续更新。。。。。。
